S. Dichiara (NASA/GSFC/UMCP) and V. D'Elia (ASDC) for the Swift team
At 06:52:27 UT, the Swift Burst Alert Telescope (BAT) triggered and located GRB 201203A (trigger=1010946) (Dichiara et al. GCN Circ. 28985). Swift slewed immediately to the burst. At the time of the trigger, the initial BAT position was 122° from the Sun (9.9 hours East) and 83° from the 92%-illuminated Moon. Table 1 contains the best reported positions from Swift.
Table 2 is a summary of GCN Circulars about this GRB from observatories other than Swift.
Standard analysis products for this burst are available at https://gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/swift_gnd_ana.html.
As reported by Sakamoto et al. (GCN Circ. 28995),
the BAT ground-calculated position is RA, Dec = 38.055, -26.505 deg which is RA(J2000) = 0
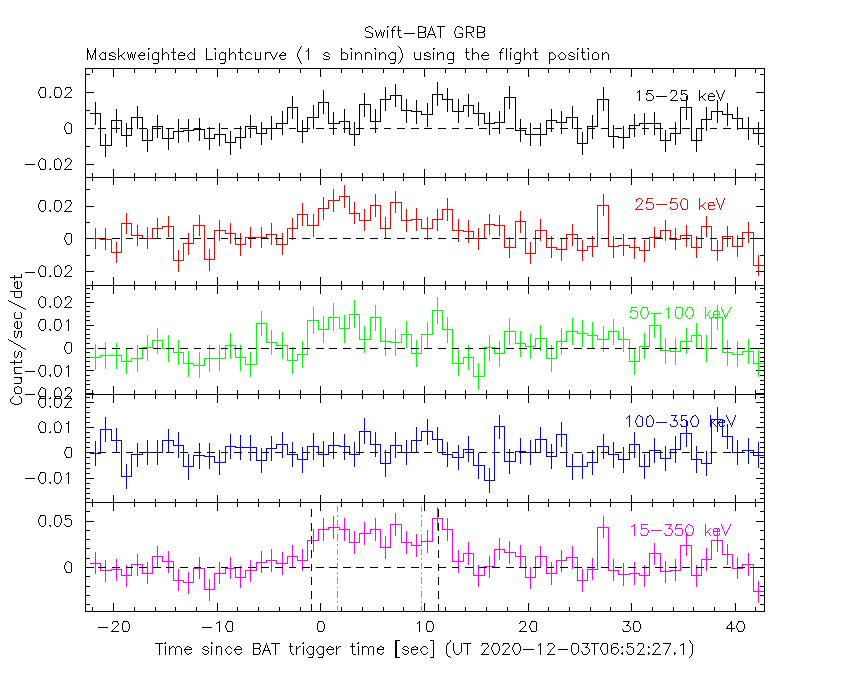
The BAT light curve (Figure 1) showed a complex structure with a duration of about ~20 s.
The time-averaged spectrum from T-2.73 to T+12.84 s is best fit by a simple power-law model.
The power law index of the time-averaged spectrum is 1.78 ± 0.26.
The fluence in the 15-150 keV band is 2.9 ± 0.5 x 1
The results of the batgrbproduct analysis are available at https://gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/notices_s/1010946/BA/.
Analysis of the initial XRT data was reported by D'Elia et al. (GCN Circ. 28990).
The light curve (Figure 2) can be modelled with a power-law decay with a decay index of α=1.4 (+1.3, -1.1).
A spectrum formed from the PC mode data can be fitted with an absorbed
power-law with a photon spectral index of 1.9 (+0.7, -0.4). The
best-fitting absorption column is consistent with the Galactic value
of 1.8 x 1
UVOT results are not available.

Figure 1. The BAT
mask-weighted light curve in the four individual and total
energy bands. The units are counts
| RA (J2000) | Dec (J2000) | Error | Note | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 |
-26°31'06.1" | 3.5" | XRT-final | UKSSDC |
| 0 |
-26°31'05.5" | 3.3" | XRT | D'Elia et al. GCN Circ. 28990 |
| 0 |
-26°30'19.2" | 1.9' | BAT-refined | Sakamoto et al. GCN Circ. 28995 |
| Band | Authors | GCN Circ. | Subject | Observatory | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical | Jelinek et al. | 28986 | FRAM-Auger optical limit | FRAM | upper limits |
| Optical | Watson et al. | 28987 | DDOTI Observations | Deca-Degree Optical Imager | |
| Optical | Zheng and Filippenko | 28988 | KAIT Optical Upper Limit | KAIT | upper limits |
| Optical | Lipunov et al. | 28991 | Swift GRB 201203A: Global MASTER-Net observations report |
MASTER | |
| Optical | Niwano et al. | 28992 | MITSuME Okayama optical upper limits | MITSuME Okayama | upper limits |
| Optical | Kumar et al. | 28993 | GROWTH-India Telescope optical upper limit. |
GROWTH-India | upper limits |
| Optical | Kumar et al. | 29030 | 1.3m DFOT, optical upper limits | Devasthal Opt.Tel. | upper limits |
| Optical | Pankov et al. | 29032 | Zeiss-1000 (Koshka observatory) optical upper limit |
Zeiss-1000 | upper limits |
December 13, 2020