J.K. Cannizzo (NASA/UMBC), A.P. Beardmore (U. Leicester) and M.H. Siegel (PSU) for the Swift team
At 06:36:24 UT, the Swift Burst Alert Telescope (BAT) triggered and located GRB 181202A (trigger=874334) (Cannizzo et al. GCN Circ. 23482). Swift slewed immediately to the burst. At the time of the trigger, the initial BAT position was 59° from the Sun (2.2 hours East) and 90° from the 26%-illuminated Moon. Table 1 contains the best reported positions from Swift, and the latest XRT position can be viewed at http://www.swift.ac.uk/xrt_positions.
Cannizzo et al. (GCN Circ. 23482) reported the discovery with UVOT of an optical afterglow. Table 2 is a summary of GCN Circulars about this GRB from observatories other than Swift.
Standard analysis products for this burst are available at https://gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/swift_gnd_ana.html.
As reported by Ukwatta et al. (GCN Circ. 23489),
the BAT ground-calculated position is RA, Dec = 280.737, 27.976 deg which is RA(J2000) = 1
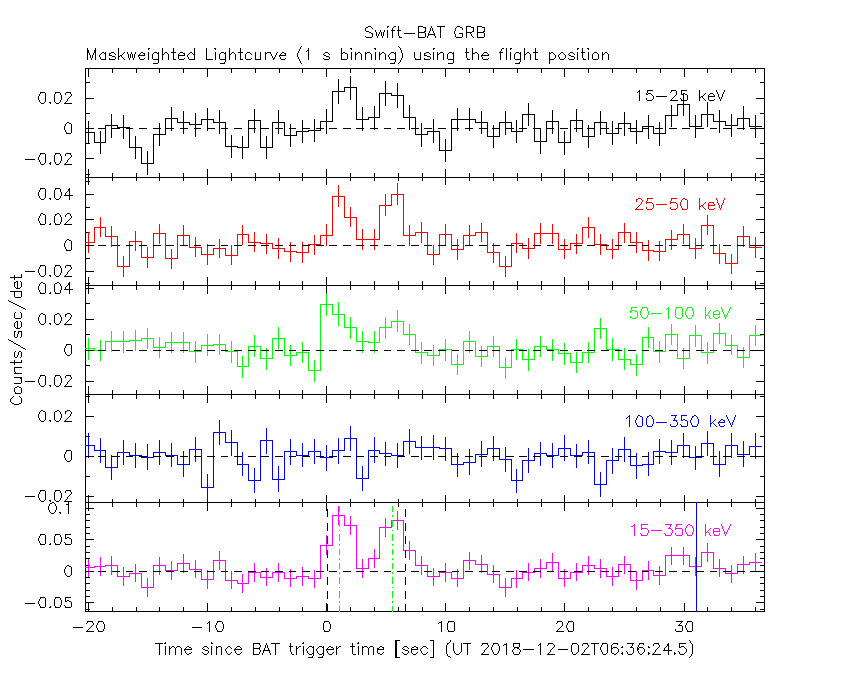
The mask-weighted light curve (Figure 1) shows a double-peaked structure that starts at ~
The time-averaged spectrum from T-0.26 to T+6.76 s is best fit by a simple power-law model.
The power law index of the time-averaged spectrum is 1.61 ± 0.24.
The fluence in the 15-150 keV band is 2.5 ± 0.4 x 1
The results of the batgrbproduct analysis are available at https://gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/notices_s/874334/BA/.
Analysis of the initial XRT data was reported by Beardmore et al. (GCN Circ. 23487). We have analysed 14 ks of XRT data for GRB 181202A, from 102 s to 161.8 ks after the BAT trigger. The data are entirely in Photon Counting (PC) mode. The enhanced XRT position for this burst was given by Evans et al. (GCN Circ. 23483).
The light curve (Figure 2) can be modelled with a power-law decay with a decay index of α=0.81 ± 0.06.
A spectrum formed from the PC mode data can be fitted with an absorbed power-law with a photon spectral index of 1.62 (+0.21, -0.14). The best-fitting absorption column is 1.77 (+0.90, -0.10) x 1
A summary of the PC-mode spectrum is thus:
Total column: 1.77 (+0.90, -0.10) x 1
Galactic foreground: 1.7 x 1
Excess significance: <1.6 σ
Photon index: 1.62 (+0.21, -0.14)
The results of the XRT team automatic analysis are available at http://www.swift.ac.uk/xrt_products/00874334.
The Swift/UVOT began settled observations of the field of GRB 181202A 86 s after the BAT trigger
(Siegel and Cannizzo GCN Circ. 23498).
A source consistent with the XRT position (Evans et al. GCN Circ. 23483) is detected in the initial UVOT exposures.
Table 3 gives preliminary
magnitudes using the UVOT photometric system
(Breeveld et al. 2011, AIP Conf. Proc., 1358, 373).
No correction has been made for the expected extinction in the Milky Way
corresponding to a reddening of

Figure 1. The BAT
mask-weighted light curve in the four individual and total
energy bands. The units are counts
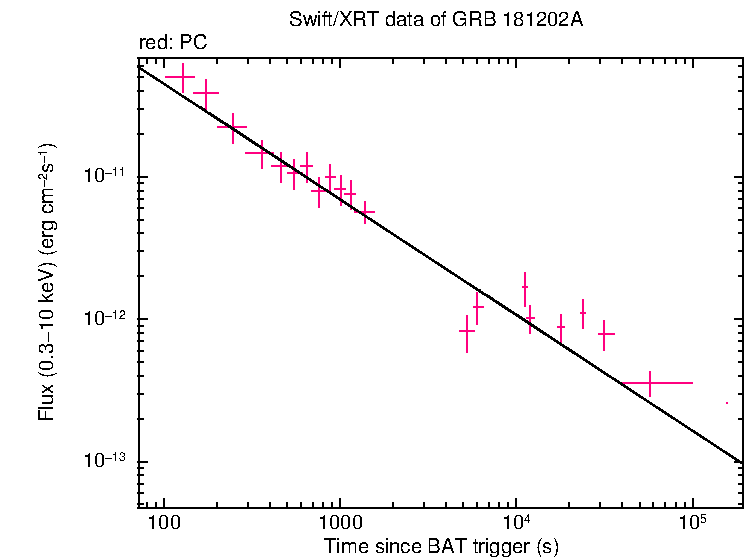
Figure 2. The XRT light curve.
Any data from a crosshatched region are not included in the fit.
| RA (J2000) | Dec (J2000) | Error | Note | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
+27°57'35.0" | 0.47" | UVOT-refined | Siegel and Cannizzo GCN Circ. 23498 |
| 1 |
+27°57'34.5" | 1.5" | XRT-final | UKSSDC |
| 1 |
+27°57'34.7" | 1.8" | XRT-enhanced | Evans et al. GCN Circ. 23483 |
| 1 |
+27°58'33.4" | 2.0' | BAT-refined | Ukwatta et al. GCN Circ. 23489 |
| Band | Authors | GCN Circ. | Subject | Observatory | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical | Lipunov et al. | 23490 | Global MASTER-Net optical observations | MASTER | upper limits |
| Optical | Watson et al. | 23496 | RATIR Optical and NIR Observations | RATIR | upper limits |
| Filter | Exp(s) | Mag | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| v | 623 | 1540 | 117 | >18.7 |
| b | 342 | 591 | 246 | 19.57 ± 0.18 |
| u (fc) | 86 | 336 | 246 | 17.67 ± 0.07 |
| w1 | 672 | 1441 | 97 | >19.6 |
| m2 | 647 | 1560 | 112 | >22.2 |
| w2 | 598 | 1516 | 117 | >20.5 |
Table 3. UVOT observations reported by Siegel and Cannizzo (GCN Circ. 23498). The start and stop times of the exposures are given in seconds since the BAT trigger. The preliminary detections and 3-σ upper limits are given. No correction has been made for extinction in the Milky Way.
December 4, 2018