E. Sonbas (Adiyaman Univ.), K.L. Page (U. Leicester) and N.P.M. Kuin (UCL-MSSL) for the Swift team
At 13:34:44 UT, the Swift Burst Alert Telescope (BAT) triggered and located GRB 190106A (trigger=882252) (Sonbas et al. GCN Circ. 23615). Swift slewed immediately to the burst. At the time of the trigger, the initial BAT position was 110° from the Sun (6.9 hours East) and 105° from the 0%-illuminated Moon. Table 1 contains the best reported positions from Swift, and the latest XRT position can be viewed at http://www.swift.ac.uk/xrt_positions.
Sonbas et al. (GCN Circ. 23615) reported the detection with UVOT of an optical afterglow. Zhu et al. (GCN Circ. 23623) determined a redshift of 0.896 from Xinglong, Xu et al. (GCN Circ. 23629) determined a redshift of 1.86 from Xinglong, and Schady et al. (GCN Circ. 23632) determined a redshift of 1.859 from VLT. Table 2 is a summary of GCN Circulars about this GRB from observatories other than Swift.
Standard analysis products for this burst are available at https://gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/swift_gnd_ana.html.
As reported by Palmer et al. (GCN Circ. 23625),
the BAT ground-calculated position is RA, Dec = 29.877, 23.839 deg, which is RA(J2000) = 0
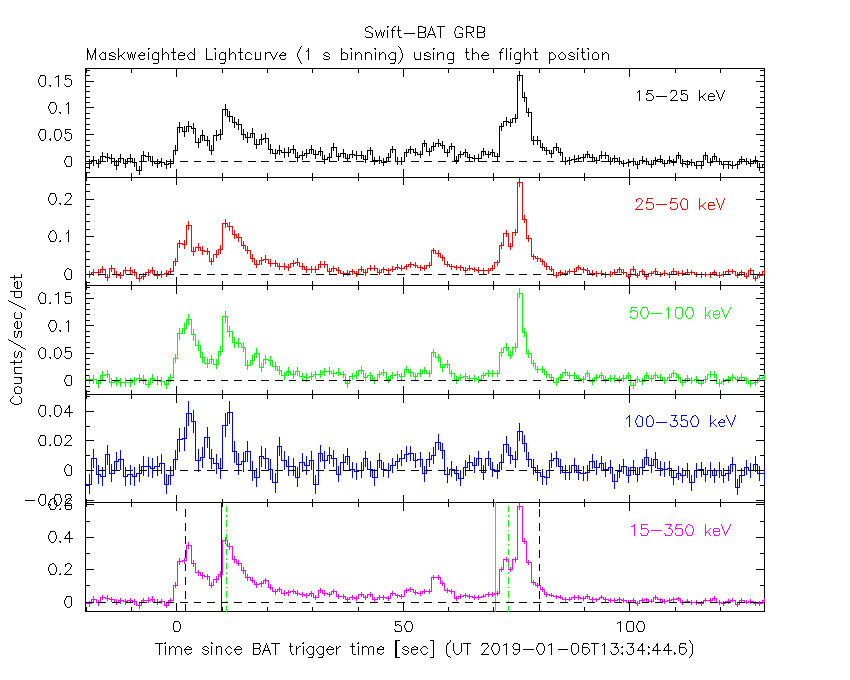
The mask-weighted light curve (Figure 1) shows it started at ~T-10s, with a pair of overlapping FRED-like peaks at ~T+2 and ~T+10 s, then a long decay and two more peaks at ~T+57 and ~T+76 s, and returning to baseline at ~T+125 s.
The time-averaged spectrum from T-0.17 to T+99.72 s is best fit by a power law with an exponential cutoff.
This fit gives a photon index 1.34 ± 0.21, and
The results of the batgrbproduct analysis are available at https://gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/notices_s/882252/BA/.
Analysis of the initial XRT data was reported by Page et al. (GCN Circ. 23633). We have analysed 35 ks of XRT data for GRB 190106A (Yurkov et al. GCN Circ. 23614), from 71 s to 878.9 ks after the BAT trigger. The data comprise 217 s in Windowed Timing (WT) mode (the first 9 s were taken while Swift was slewing) with the remainder in Photon Counting (PC) mode. The enhanced XRT position for this burst was given by Goad et al. (GCN Circ. 23619).
The late-time light curve (Figure 2) (from T0+11.7 ks) can be modelled with an initial power-law decay with an index of α=1.01 (+0.12, -0.07), followed by a break at T+69.2 ks to an α of 1.49 (+0.14, -0.13).
A spectrum formed from the WT mode data can be fitted with an absorbed power-law with a photon spectral index of 2.06 (+0.06, -0.05). The best-fitting absorption column is 1.9 ± 1.1 x 1
A summary of the PC-mode spectrum is thus:
Galactic foreground: 1.0 x 1
Intrinsic column: 1.0 (+1.6, -0.0) x 1
Photon index: 1.95 (+0.09, -0.06)
The results of the XRT team automatic analysis are available at http://www.swift.ac.uk/xrt_products/00882252.
The Swift/UVOT began settled observations of the field of GRB 190106A 90 s after the BAT trigger
(Kuin and Sonbas GCN Circ. 23626).
A source consistent with the XRT position (Goad et al. GCN Circ. 23619) is detected in the initial UVOT exposures.
Table 3 gives preliminary
magnitudes using the UVOT photometric system
(Breeveld et al. 2011, AIP Conf. Proc., 1358, 373).
No correction has been made for the expected extinction in the Milky Way
corresponding to a reddening of

Figure 1. The BAT
mask-weighted light curve in the four individual and total
energy bands. The units are counts
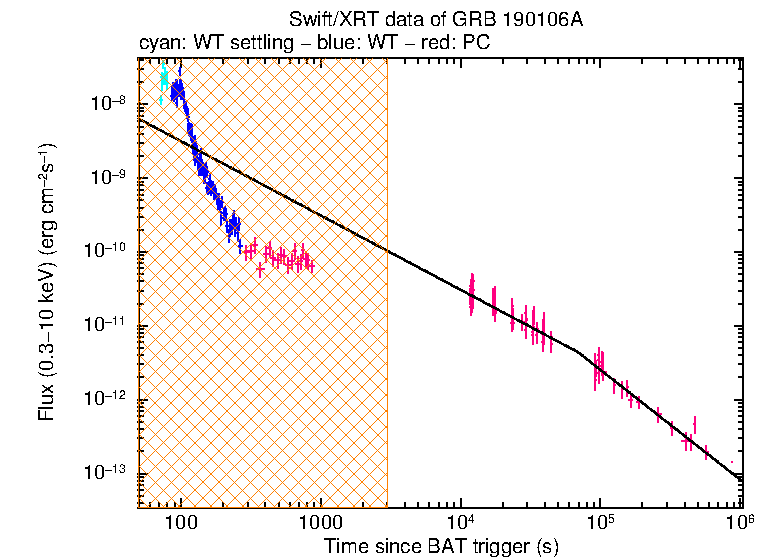
Figure 2. The XRT light curve.
Any data from a crosshatched region are not included in the fit.
| RA (J2000) | Dec (J2000) | Error | Note | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 |
+23°50'43.9" | 0.42" | UVOT-refined | Kuin and Sonbas GCN Circ. 23626 |
| 0 |
+23°50'43.8" | 1.4" | XRT-final | UKSSDC |
| 0 |
+23°50'43.6" | 1.8" | XRT-enhanced | Goad et al. GCN Circ. 23619 |
| 0 |
+23°50'20.8" | 1.0' | BAT-refined | Palmer et al. GCN Circ. 23625 |
| Band | Authors | GCN Circ. | Subject | Observatory | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optical | Yurkov et al. | 23614 | SWIFT GRB190106.57 Global MASTER-Net OT detection |
MASTER | detection |
| Optical | Lipunov et al. | 23616 | MASTER Amur OT detection | MASTER | detection |
| Optical | Itoh et al. | 23617 | MITSuME Akeno optical observation | MITSuME Akeno | |
| Optical | Mao et al. | 23618 | GMG detection | Gao-Mei-Gu | detection |
| Optical | Reva et al. | 23620 | TSHAO optical observations | Zeiss-1000 | |
| Optical | Xin et al. | 23622 | GWAC-F60B optical detection | Xinglong Obs. | detection |
| Optical | Zhu et al. | 23623 | Xinglong-2.16m spectroscopy | Xinglong | spectroscopy |
| Optical | Quadri | 23624 | Bassano Bresciano Observatory optical detection |
Bassano Bresciano Obs. | detection |
| Optical | Hu et al. | 23627 | BOOTES-4/MET optical observations | BOOTES-4 | |
| Optical | Noschese et al. | 23628 | OASDG optical observations | S.Di Giacomo Obs. | |
| Optical | Xu et al. | 23629 | update of the Xinglong-2.16m spectroscopy |
Xinglong | spectroscopy |
| Optical | Mao et al. | 23630 | GMG spectral results | Gao-Mei-Gu | |
| Optical | Schady et al. | 23632 | VLT/X-shooter redshift confirmation | VLT | redshift |
| Optical | Mao et al. | 23634 | GMG photometry in the 2nd night | Gao-Mei-Gu | |
| Optical | Chakrabarti et al. | 23635 | IERCOO/ICSP optical observation | ||
| Optical | Zhu et al. | 23636 | NEXT-0.6m and Xinglong-2.16m photometric single powerlaw decay |
Xinglong | light curve |
| Optical | Reva et al. | 23638 | continued TSHAO optical observations | Zeiss-1000 | |
| Optical | Belkin et al. | 23640 | Mondy optical observations | Mondy | light curve |
| Optical | Izzo et al. | 23660 | Liverpool Telescope observations | Liverpool Telescope | detection |
| Optical | Belkin et al. | 23661 | optical observations, possible jet break detection |
Mondy | possible detection |
| Optical | Blazek et al. | 23665 | OSN Afterglow Observations | Obs.de Sierra Nevada | detection |
| Optical | Mao et al. | 23668 | GMG continued observation | Gao-Mei-Gu | |
| Optical | Dichiara et al. | 23744 | Discovery Channel Telescope observations | Discovery Channel | |
| Gamma-ray | Tsvetkova et al. | 23637 | Konus-Wind observation | Konus-Wind | Duration=~79 seconds Fluence=1.12(-0.17,+0.25)x1 |
| Filter | Exp(s) | Mag | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| white | 90 | 240 | 147 | 16.64 ± 0.03 |
| v | 633 | 653 | 20 | 16.54 ± 0.16 |
| b | 559 | 579 | 20 | 16.70 ± 0.09 |
| u | 304 | 553 | 246 | 15.97 ± 0.03 |
| w1 | 682 | 702 | 20 | 17.36 ± 0.29 |
Table 3. UVOT observations reported by Kuin and Sonbas (GCN Circ. 23626). The start and stop times of the exposures are given in seconds since the BAT trigger. The preliminary detections and 3-σ upper limits are given. No correction has been made for extinction in the Milky Way.
January 17, 2019